Understanding Big Toe Pain: Common Causes and How to Find Relief
Big toe pain can be incredibly uncomfortable and disruptive to daily life. Whether it’s a sharp, stabbing sensation or a dull ache, pain in the big toe can stem from various underlying causes. In this blog post, we’ll explore two of the most common reasons for big toe pain, shedding light on what might be causing your discomfort and offering insights into potential treatments.

Hallux Rigidus: Understanding a Stiff, Painful Big Toe
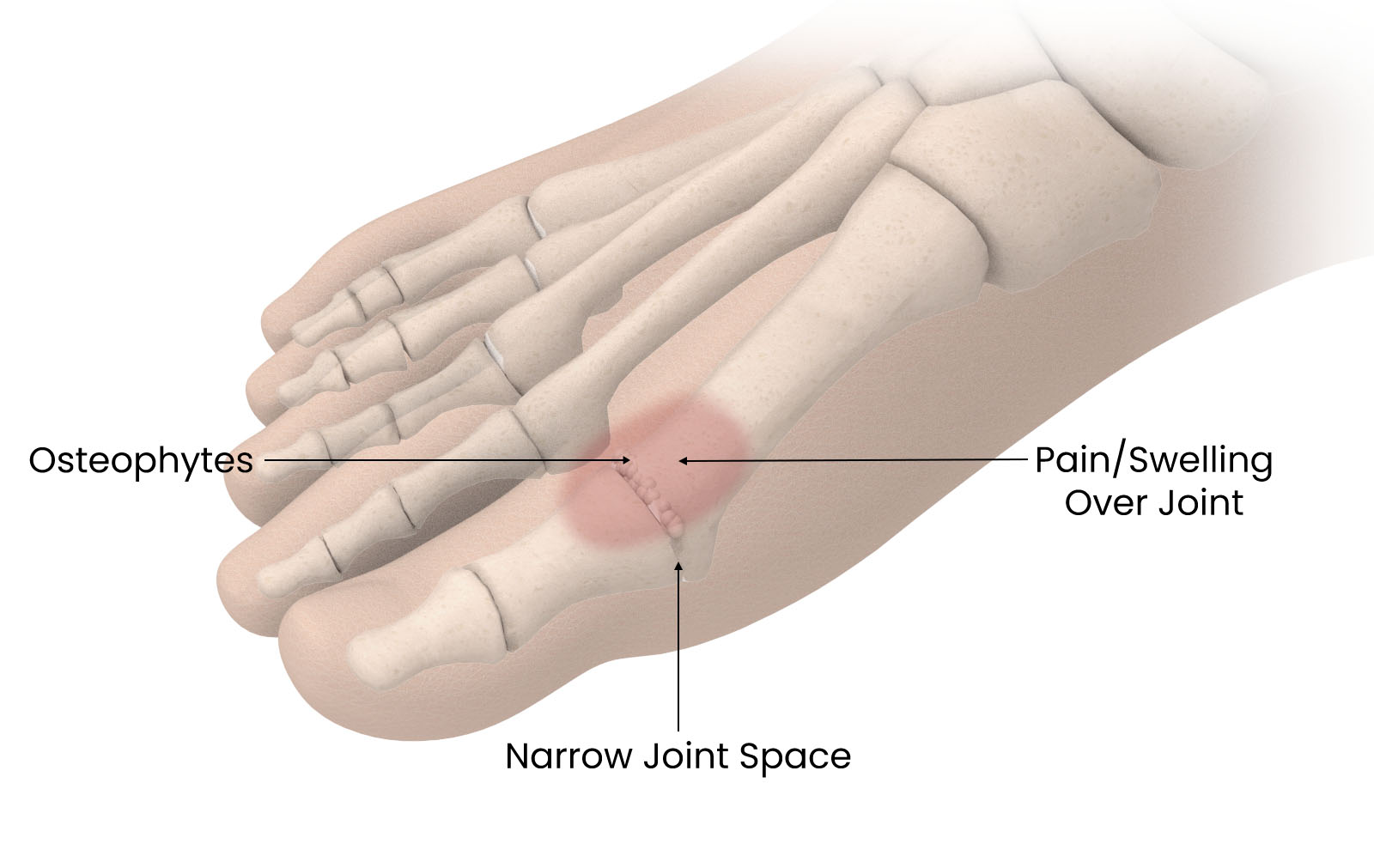
Hallux rigidus is a condition that affects the big toe joint, causing stiffness and limited movement. It is a form of degenerative arthritis that primarily affects the joint at the base of the big toe, medically referred to as the first metatarsophalangeal joint. This condition often leads to pain, decreased mobility, and difficulty in performing activities that require bending the big toe, such as walking or running. In this post, we’ll delve into the details of hallux rigidus, its causes, symptoms, and potential treatment options.
Causes of Hallux Rigidus:
Hallux rigidus typically develops due to the gradual wear and tear of the cartilage that cushions the joint surfaces. As the cartilage deteriorates over time, the bones in the joint may start rubbing against each other, leading to pain, inflammation, and limited mobility. Several factors can contribute to the development of hallux rigidus:
- Age: The risk of developing hallux rigidus increases with age, as the joint cartilage naturally undergoes degeneration over time.
- Genetics: A family history of hallux rigidus or other foot conditions can predispose individuals to this condition.
- Foot Structure: An individual’s foot anatomy, such as having a first metatarsal bone that is longer than usual, can increase the likelihood of developing hallux rigidus.
- Injury or Trauma: A previous injury or trauma to the big toe joint, such as a fracture or dislocation, can accelerate the onset of hallux rigidus.
Symptoms of Hallux Rigidus:
The primary symptoms of hallux rigidus revolve around pain and stiffness in the big toe joint. Common symptoms include:
- Stiffness: Gradual loss of flexibility in the big toe joint, making it challenging to bend the toe.
- Pain: Pain at the base of the big toe, particularly during activities that involve toe movement or pressure on the joint.
- Swelling: Inflammation around the joint may cause swelling and tenderness.
- Difficulty Walking: As the condition progresses, walking, running, and even standing may become increasingly uncomfortable.
- Enlarged Bone: Over time, bone spurs (small bony growths) may develop around the affected joint, leading to further pain and limited motion.
Treatment and Management:
The management of hallux rigidus depends on the severity of the condition and its impact on an individual’s daily activities. Some treatment options include:
- Footwear: Wearing shoes with a wide toe box and good arch support can help alleviate pressure on the joint.
- Orthotics: Custom-made or over-the-counter shoe inserts can help improve foot mechanics and reduce strain on the big toe joint.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be recommended to manage pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Specific exercises can improve joint mobility, strengthen surrounding muscles, and enhance gait.
- Corticosteroid Injections: Injections of corticosteroids into the joint can provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation.
- Surgical Intervention: In cases where conservative methods are ineffective, surgical options like joint replacement, cheilectomy (removal of bone spurs) or joint fusion may be considered to alleviate pain and restore functionality. If looking to maintain joint motion, it is important to choose an implant with a long history of successful clinical outcomes. The BioPro Hemi Toe Implant has over 70 years of clinical history and is supported by published studies worldwide.
Hallux rigidus can significantly impact an individual’s mobility and quality of life. Early recognition of symptoms and appropriate intervention can help manage pain, preserve joint function, and prevent further deterioration. If you suspect you have hallux rigidus or are experiencing persistent big toe pain and stiffness, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional, preferably a podiatrist or orthopedic specialist. You can use BioPro’s Find a Surgeon tool to find a surgeon in your area.
Bunions: Understanding the Bump at the Base of Your Big Toe
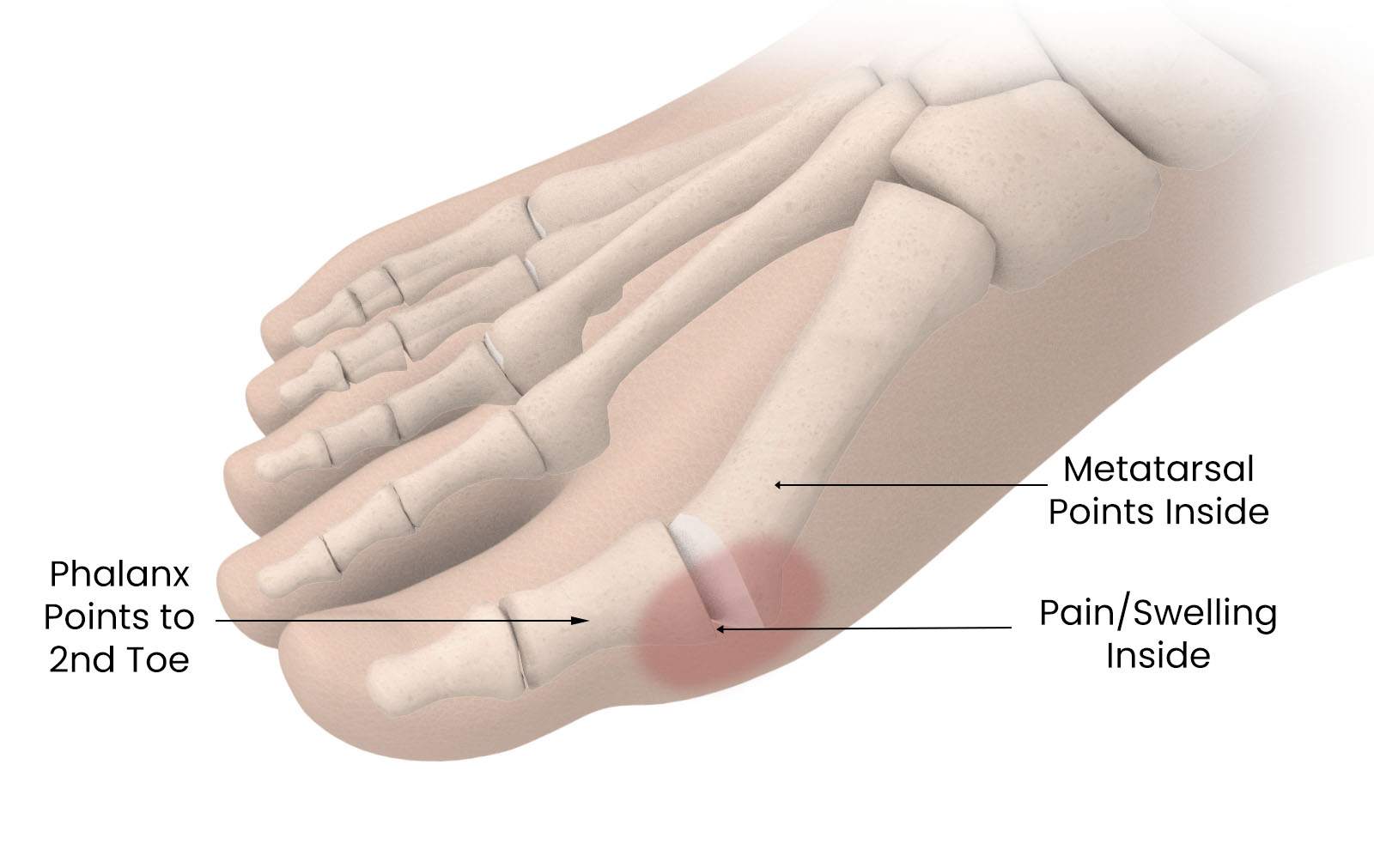
Bunions, medically known as “hallux valgus,” are a common foot condition characterized by the gradual misalignment of the big toe joint. This leads to the formation of a bony bump at the base of the big toe. Bunions can cause discomfort, pain, and changes in foot structure.
Causes of Bunions:
Bunions often develop due to a combination of genetic predisposition and lifestyle factors. Some common factors that contribute to bunion formation include:
- Genetics: If bunions run in your family, you might be more likely to develop them. Genetic factors can influence foot structure and mechanics, which can contribute to bunion formation.
- Footwear: Wearing tight, narrow, or ill-fitting shoes, especially those with high heels, can increase pressure on the front of the foot and contribute to bunion development.
- Foot Mechanics: Abnormal foot mechanics, such as overpronation (excessive inward rolling of the foot while walking), can lead to the misalignment of the big toe joint over time.
- Arthritis: Certain types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, can increase the risk of bunion formation.
- Injury: Trauma or injury to the foot can lead to changes in joint alignment that contribute to bunion development.
Symptoms of Bunions:
Bunions can cause a range of symptoms, which may vary in severity. Common symptoms include:
- Bony Bump: The most visible sign of a bunion is the bony bump at the base of the big toe joint.
- Toe Misalignment: The big toe may angle towards the second toe, causing the joint to protrude outward.
- Pain: The bunion can cause pain or discomfort, especially when walking, standing, or wearing tight shoes.
- Swelling: Inflammation around the bunion area can lead to swelling and redness.
- Corns and Calluses: The friction between the bunion and shoes can lead to the formation of corns and calluses.
- Limited Toe Movement: As the bunion progresses, it can restrict the range of motion of the big toe.
Treatment and Management:
The management of bunions depends on the severity of the condition and the impact on an individual’s quality of life. Here are some common approaches to treating and managing bunions:
- Footwear: Wearing shoes with a wide toe box and adequate arch support can help alleviate pressure on the bunion and prevent further irritation.
- Padding and Orthotics: Padded inserts and custom orthotic devices can provide cushioning and support, helping to reduce friction and pressure on the bunion.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications may help manage pain and inflammation.
- Toe Spacers: These devices can help separate the big toe from the second toe, relieving pressure on the joint.
- Physical Therapy: Specific exercises can improve foot mechanics, strengthen muscles, and enhance joint flexibility.
- Surgical Intervention: In cases of severe pain or deformity that significantly affect daily activities, surgical options like bunionectomy (removal of the bony bump) may be considered.
Bunions are a common foot condition that can cause discomfort and affect your quality of life. Early intervention and proper care, including appropriate footwear and conservative treatments, can help manage symptoms and prevent the condition from worsening. If you suspect you have a bunion or are experiencing persistent foot pain, consulting a healthcare professional, preferably a podiatrist, is crucial. By addressing bunions proactively, you can work towards maintaining your foot health and enjoying a more comfortable and active lifestyle.
Sesamoiditis: Understanding and Managing Big Toe Pain
Sesamoiditis is a painful condition that affects the sesamoid bones located beneath the big toe joint. These small, pea-sized bones are embedded within tendons and help facilitate smooth joint movement, acting as pulleys. When the tendons surrounding the sesamoid bones become inflamed or irritated, it leads to sesamoiditis, causing significant discomfort in the ball of the foot.
Causes of Sesamoiditis:
Sesamoiditis often develops due to overuse or repetitive stress on the sesamoid bones and their surrounding tendons. Athletes engaging in activities that involve high impact or excessive pressure on the forefoot, such as dancing, running, or jumping, are particularly susceptible to this condition. Other contributing factors include:
- Improper Footwear: Wearing shoes that lack proper cushioning or have inadequate arch support can increase the risk of sesamoiditis.
- Foot Structure: Individuals with high arches or those with a specific foot structure that places more stress on the sesamoid bones may be prone to developing sesamoiditis.
- Sudden Increase in Activity: A sudden spike in physical activity levels or intensity can strain the sesamoid bones and lead to inflammation.
- Trauma: Direct trauma to the sesamoid area, such as stubbing the toe or experiencing a forceful impact, can trigger sesamoiditis.
Symptoms of Sesamoiditis:
Sesamoiditis typically manifests as pain and discomfort under the big toe joint, specifically in the ball of the foot. Common symptoms include:
- Localized Pain: Pain is usually concentrated beneath the big toe joint and may worsen when walking, running, or engaging in activities that involve pushing off the toes.
- Swelling and Tenderness: Inflammation of the sesamoid area can lead to swelling and tenderness.
- Difficulty in Toe Movement: Pain and inflammation can limit the ability to bend or move the big toe without discomfort.
Treatment and Management:
Addressing sesamoiditis involves a combination of self-care strategies and medical interventions. Here are some approaches to consider:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Giving the affected foot adequate rest and avoiding activities that exacerbate the pain can help reduce inflammation.
- Ice and Elevation: Applying ice to the painful area and elevating the foot can help alleviate swelling and discomfort.
- Cushioned Footwear: Wearing shoes with ample cushioning and proper arch support can alleviate pressure on the sesamoid bones and promote healing.
- Orthotics: Custom or over-the-counter orthotic inserts can provide additional support and cushioning to the foot.
- Medications: Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications like ibuprofen may help manage pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can guide you through exercises to improve foot strength, flexibility, and mechanics, reducing strain on the sesamoid bones.
- Padding and Taping: Your healthcare provider may recommend padding or taping techniques to relieve pressure on the sesamoid area.
In severe cases where conservative methods fail to provide relief, a medical professional might consider more advanced treatments, including corticosteroid injections or, rarely, surgical removal of the affected sesamoid bone.
Sesamoiditis can be a painful and frustrating condition, but with proper care and attention, it can be managed effectively. Early intervention, such as adjusting activity levels, wearing appropriate footwear, and following self-care measures, can help prevent the condition from worsening. If you’re experiencing persistent big toe pain or suspect sesamoiditis, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan. By taking proactive steps, you can work towards alleviating pain and getting back to your active lifestyle.
Learn what treatments may be right for you.
Find a Surgeon
To locate experienced surgeons in your area, please complete the form to access our surgeon locator. Alternatively, you can email us at info@bioproimplants.com or call (810) 982-7777.
Consult with your surgeon
Discuss all your possible treatment options and expectations after surgery.
Undergoing joint replacement
Joint replacement surgery with the BioPro Hemi Toe is an outpatient procedure. You should be in and out in one day and on the road to recovery.